HONEY PROCESSING
Introduction
Beekeeping is an ideal activity for development as a subsidiary occupation providing supplementary income. Beekeeping is feasible in areas where adequate bee flora is available for a minimum period of 6 months. Honey produced by Indian hive bees is collected by a modern extractor. The extracted honey contains hemophilic yeasts, which causes fermentation and destroy the quality of honey. To maintain the qualitative and quantitative value of honey the processing in the modern Honey Processing plant is essential.
Product & Its Application
For centuries, honey has been used as a natural sweetening agent and in the preparation of confectionaries. It has vast application in the pharmaceutical industry, and it is also considered as medicine by Ayurved. It is popularly used as a household cure for cough and hence used as a vehicle for medicines in many popular brands of Cough Syrup. It is a preferred consumable for people on dieting. Honey is also used for making lozenges. However, it is mostly sold in glass Jars as pure honey. In bottled honey normally moisture content of honey is reduced. Good quality honey has high demand in the international market and it has the potential to generate substantial foreign exchange for the Country.
Desired Qualifications for Promoter
Do not require any specific qualification.
Industry Lookout and Trends
Approximately 130 million pounds of honey is imported into the United States each year. This is a significant amount, considering it is over half of domestic production each year. Honey is produced in other countries for export to the United States because it is a low-tech, low capital business. The three leading exporters of honey to the United States are Argentina, China, and Canada. Imports of honey into the United States have a large effect on the price of honey received by domestic honey producers. Even Sioux Bee Honey Cooperative imports honey into the United States for packing and sale to the retail consumer. This is not popular with all consumers as some foreign honey enters the United States having been mixed with corn syrup to add volume.
The National Honey Board and others in the honey industry are trying to find a marketing niche for honey in the years to come. One area that they have focused plenty of generic advertising dollars on is the potential health-promoting effects of honey. There is research being conducted currently that is examining honey’s role as a burn remedy, ulcer medication, and antioxidant, laxative and as a wound healer. Honey is also popular with some people in the alternative medicine arena and with people who are interested in organic food. Some people believe that honey is good for allergies or they believe that consuming the wax from the comb promotes overall general health. Some people even attempt to treat nervous system disorders, muscular disorders and arthritis with bee stings. Even though the overall trend in the United States is toward an alternative type of medicine, it does not appear that this trend will increase demand for honey very much over the next few years. Without some kind of solid scientific study by the FDA confirming any possible health benefits of eating honey, it would seem that the industry should concentrate on promoting honey as a natural food or for its taste. Banking on an advertising strategy that depends on changing attitudes about health may be risky.
Market Potential
The key target market would be:
• Ayurvedic Industry
• Food processing Industry
• Exports
• Domestic Retail Market
Quality control and standardization of honey are essential for selling in the international market. For export to European Union (EU) and some other countries, it’s mandatory to control the level of pesticides and insecticidal residue in the finished product. Further, some countries insist on a certificate validating the purchase of honey from the disease-free colony. Presently there is no disease surveillance system in place and honey collected by tribal is stored unscientifically and in an unhygienic manner which increases the propensity for contamination and deterioration and renders the product unfit for exports.
Honey is a major consumable in the international market both as a food item as well as in industries such as Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics and Confectionary. The demand is especially high for refined, high-quality honey free from pesticides, insecticides and other agro-chemicals.
China is the world-leading producer as well as exporter of honey.
In the domestic market, a very little amount of honey is used for personal consumption, while the majority is utilized by the pharmaceutical and confectionary industry. With changing lifestyles and increasing health consciousness, honey is been increasing consumed as health food. This is likely to drive domestic demand in future.
Raw Material Requirements
Only honey and basic packing material (bottle, lids and labels) are required for raw material.
Manufacturing Process
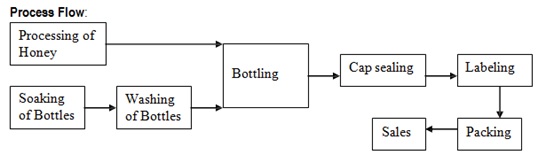
Honey collected from Beekeepers is tested and fed into the Honey Processing plant. The plant removes excess moisture and wax in Honey to yield thick honey. The processed honey is immediately bottled in clean wide-mouthed bottles. It is then sealed by PP Caps. Bottles are wiped dry and labelled. Filled, sealed & labelled bottles are then packed in labelled cardboard boxes.
Manpower Requirement
Sr. No. | Designation of Employees | Salary Per Person | Monthly Salary INR | Number of employees required | ||||
|
|
|
| Year-1 | Year-2 | Year-3 | Year-4 | Year-5 |
1 | Un Skilled Workers | 8,000.00 | 16,000.00 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
2 | Accountant | 8,000.00 | 8,000.00 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
3 | Store Keeper | 6,000.00 | 6,000.00 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
4 | Sales Supervisor | 9,000.00 | 9,000.00 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
5 | Security Personnel | 6,500.00 | 6,500.00 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
6 | Manager | 20,000.00 | 20,000.00 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
7 | Skilled Labour (Operator - 1, Technical Staff - 2) | 10,000.00 | 10,000.00 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
Total |
| 65,500.00 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | |
Implementation Schedule
The project can be implemented in 13 months' time as detailed below:
Sr. No. | Activity | Time Required (in months) |
1 | Acquisition of premises | 3.00 |
2 | Construction (if applicable) | 5.00 |
3 | Procurement & installation of Plant & Machinery | 2.00 |
4 | Arrangement of Finance | 2.00 |
5 | Recruitment of required manpower | 1.00 |
Total time required (some activities shall run concurrently) | 13.00 |
Cost of Project
The project shall cost INR 35 lacs as detailed below:
Sr. No. | Particulars | INR in Lacs |
1 | Land | 7.50 |
2 | Building | 3.20 |
3 | Plant & Machinery | 15.50 |
4 | Furniture, Electrical Installations | 1.00 |
5 | Other Assets including Preliminary / Pre-operative expenses | 1.55 |
6 | Margin for Working Capital | 6.25 |
| Total | 35.00 |
Means of Finance
Bank term loans are assumed @ 60% of fixed assets. The proposed funding pattern is as under:
Sr. No. | Particulars | INR in Lacs |
1 | Promoter's contribution | 8.75 |
2 | Bank Finance | 26.25 |
| Total | 35.00 |
Working Capital Calculation
The project requires working capital of INR 6.25 lacs as detailed below:
Sr. No. | Particulars | Gross Amt | Margin % | Margin Amt | Bank Finance |
1 | Inventories | 3.13 | 0.25 | 0.78 | 2.34 |
2 | Receivables | 1.56 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 1.17 |
3 | Overheads | 1.56 | 100% | 1.56 | 0.00 |
4 | Creditors | - |
| 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Total | 6.25 |
| 2.73 | 3.52 |
Machinery Required :
A detail of important machinery is given below:
Sr. No. | Particulars | UOM | Qty | Rate (INR) | Value (INR in Lacs) | |
1 | Honey Processing Plant | NOS. | 1 | 1,200,000.00 | 12.00 | |
2 | Storage Tanks |
| 1 | 150,000.00 | 1.50 | |
3 | Bottle washing, drying and filling machine |
| 1 | 150,000.00 | 1.50 | |
4 | Honey handling equipment |
| 1 | 50,000.00 | 0.50 | |
| sub-total Plant & Machinery |
|
|
| 15.50 | |
Sr. No. | Particulars | UOM | Qtty | Rate (INR) | Value | |
| Furniture / Electrical installations |
|
|
|
| |
a) | Office furniture | LS | 1 | 50000 | 0.50 | |
b) | Stores Almirah | LS | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | |
c) | Computer & Printer | L. S. | 1 | 50000 | 0.50 | |
| subtotal |
|
|
| 1.00 | |
| Other Assets |
|
|
|
| |
a) | preliminary and preoperative |
|
|
| 1.55 | |
| sub-total Other Assets |
|
|
| 1.55 | |
| Total |
|
|
| 18.05 | |
All the machines and equipment are available from local manufacturers. The entrepreneur needs to ensure proper selection of product mix and proper type of machines and tooling to have modern and flexible designs. It may be worthwhile to look at reconditioned imported machines, dies and tooling. Some of the machinery and dies and tooling suppliers are listed here below:
1. Fry-Tech Food Equipments Private Limited
S. No. 4, Raviraj Industrial Estate,
Bhikhubhai Mukhi Ka Kuwa Bharwadvash,
Ramol, Ahmedabad - 380024,
Gujarat, India
2. Hindustan Vibrotech Pvt. Ltd.
Office No. 2, Ground Floor,
Vrindavan Building, Vile Parle East,
Mumbai – 400057,
Maharashtra, India
3. Electrons cooling systems Pvt. Ltd.
S-27, SIDCO Industrial Estate
Kakkalur Industrial Estate
Tiruvallur – 602003,
New Delhi – 110085,
Tamil Nadu, India
4. Springboard Enterprises India Ltd.
1st, 2nd & 3rd Floor,
Plot No. 7, 8 & 9,
Garg Shopping Mall,
Service Centre , Rohini Sector 2
Delhi, India
5. Flour Tech Engineers Private Limited
Plot No. 182, Sector 24,
Faridabad - 121005,
Haryana, India
6. P Square Technologies
3, Swami Mahal,
Gurunanak Nagar,
Off. Shankarsheth Road Bhavani Peth,
Pune - 411002,
Maharashtra, India
7. Ricon Engineers
10 To 13, Bhagwati Estate,
Near Amraiwadi Torrent Power,
Behind Uttam Dairy,
Rakhial, Ahmedabad - 380023,
Gujarat, India
Profitability Calculations
Sr. No. | Particulars | UOM | Year-1 | Year-2 | Year-3 | Year-4 | Year-5 |
1 | Capacity Utilization | % | 60% | 70% | 80% | 90% | 100% |
2 | Sales | INR In Lacs | 28.80 | 33.60 | 38.40 | 43.20 | 48.00 |
3 | Raw Materials & Other direct inputs | INR In Lacs | 17.12 | 19.98 | 22.83 | 25.69 | 28.54 |
4 | Gross Margin | INR In Lacs | 11.68 | 13.62 | 15.57 | 17.51 | 19.46 |
5 | Overheads except interest | INR In Lacs | 8.38 | 8.91 | 9.96 | 10.27 | 10.48 |
6 | Interest @ 10 % | INR In Lacs | 2.63 | 2.63 | 1.75 | 1.31 | 1.05 |
7 | Depreciation @ 30 % | INR In Lacs | 10.85 | 7.75 | 5.43 | 3.88 | 3.49 |
8 | Net Profit before tax | INR In Lacs | -10.18 | -5.66 | -1.56 | 2.06 | 4.44 |
The basis of profitability calculation:
This unit will have a 19,200 Kg/Annum capacity (per day 50 kg average). The growth of selling capacity will be increased 10% per year. (This is assumed by various analysis and study; it can be increased according to the selling strategy.)
Energy Costs are considered at Rs 7 per Kwh and fuel cost is considered at Rs. 65 per liter. The depreciation of plant is taken at 10-12 % and Interest costs are taken at 14 -15 % depending on type of industry.
Breakeven Analysis
The project shall reach cash break-even at 59.25% of projected capacity as detailed below:
Sr. No. | Particulars | UOM | Value |
1 | Sales at full capacity | INR In Lacs | 48.00 |
2 | Variable costs | INR In Lacs | 28.54 |
3 | Fixed costs incl. interest | INR In Lacs | 11.53 |
4 | BEP = FC/(SR-VC) x 100 = | % of capacity | 59.25% |
Statutory / Government Approvals:
The Ministry of Food Processing Industries has been operating several plan schemes for the development of the processed food sector in the country during the 10th Plan. One of the schemes relates to the Technology Up-gradation/ Establishment/ Modernization of food processing industries.
The Indian food processing industry is regulated by several laws which govern the aspects of sanitation, licensing and other necessary permits that are required to start up and run a food business. The legislation that dealt with food safety in India was the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, 1954 (hereinafter referred to as " PFA "). The PFA had been in place for over five decades and there was a need for change due to varied reasons which include the changing requirements of our food industry. The act brought into force in place of the PFA is the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (hereinafter referred to as " FSSA ") that overrides all other food related laws.
FSSA initiates harmonization of India's food regulations as per international standards. It establishes a new national regulatory body, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (hereinafter referred to as " FSSAI "), to develop science based standards for food and to regulate and monitor the manufacture, processing, storage, distribution, sale and import of food so as to ensure the availability of safe and wholesome food for human consumption. Entrepreneur may contact State Pollution Control Board where ever it is applicable.
All food imports will therefore be subject to the provisions of the FSSA and rules and regulations which as notified by the Government on 5th of August 2011 will be applicable.
Key Regulations of FSSA
A. Packaging and Labelling
B. Signage and Customer Notices
C. Licensing Registration and Health and Sanitary Permits
Backward and Forward Integrations
The objective of the scheme is to provide effective and seamless backward and forward integration for the processed food industry by plugging the gaps in supply chain in terms of availability of raw material and linkages with the market. Under the scheme, financial assistance is provided for setting up of primary processing centres/ collection centres at farm gate and modern retail outlets at the front end along with connectivity through insulated/ refrigerated transport.
The Scheme is applicable to perishable horticulture and non-horticulture produce such as, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, meat, poultry, fish, Ready to Cook Food Products, Honey, Coconut, Spices, Mushroom, Retails Shops for Perishable Food Products etc. The Scheme would enable linking of farmers to processors and the market for ensuring remunerative prices for agri produce.
The scheme is implemented by agencies/ organizations such as Govt. / PSUs/ Joint Ventures/ NGOs/ Cooperatives/ SHGs / FPOs / Private Sector / individuals etc.
Backward Linkage:
• Integrated Pack-house(s) (with mechanized sorting & grading line/ packing line/ waxing line/ staging cold rooms/cold storage, etc.)
• Pre Cooling Unit(s)/ Chillers
• Reefer boats
• Machinery & equipment for minimal processing and/or value addition such as cutting, dicing, slicing, pickling, drying, pulping, canning, waxing, etc.
• Machinery & equipment for packing/ packaging.
Forward Linkage:
• Retail chain of outlets including facilities such as frozen storage/ deep freezers/ refrigerated display cabinets/cold room/ chillers/ packing/ packaging, etc.
• Distribution centre associated with the retail chain of outlets with facilities like cold room/ cold storage/ ripening chamber.
Training Centers and Courses
There are few specialized Institutes that provide degree certification in Food Technology, few of the most famous and authenticated Institutions are as follows:
• Indian Institute of Food Science & Technology,
Plot No.1, Near Maa-Baap ki Dargah, Opp to Nath Seeds,
Paithan Road Aurangabad
Aurangabad - 431005
Maharashtra, India
• MIT College of Food Technology, Pune
Gate.No.140, Raj Baugh Educational Complex,
Pune Solapur Highway,
Loni Kalbhor, Pune – 412201
Maharashtra, India
• CSIR - Central Food Technological Research Institute (CFTRI)
Cheluvamba Mansion, Opp. Railway Museum,
Devaraja Mohalla, CFTRI Campus, Kajjihundi, Mysuru
Karnataka – 570020
Udyamimitra portal ( link: www.udyamimitra.in ) can also be accessed for handholding services viz. application filling/project report preparation, EDP, financial Training, Skill Development, mentoring etc.
Entrepreneurship program helps to run a business successfully is also available from Institutes like Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India (EDII) and its affiliates all over India.
Comments
Post a Comment